Overview¶
Medici is designed to support any data format and multiple research domains and contains three major extension points: preprocessing, processing and previewing. Information in Medici is organized using the following data model:
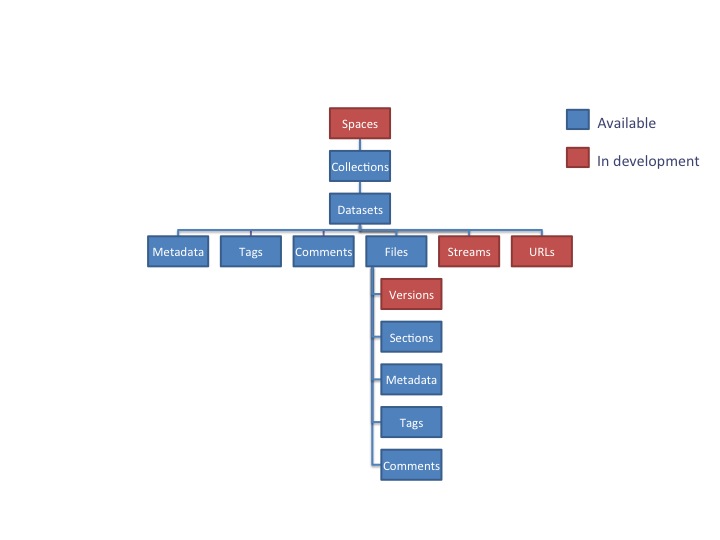
When new data is added to the system, whether it is via the web interface or through the RESTful API, preprocessing is off-loaded to extraction services in charge of extracting appropriate data and metadata. The extraction services attempt to extract information and run preprocessing steps based on the type of the data just uploaded. Extracted information is then written back to the repository using appropriate API endpoints.
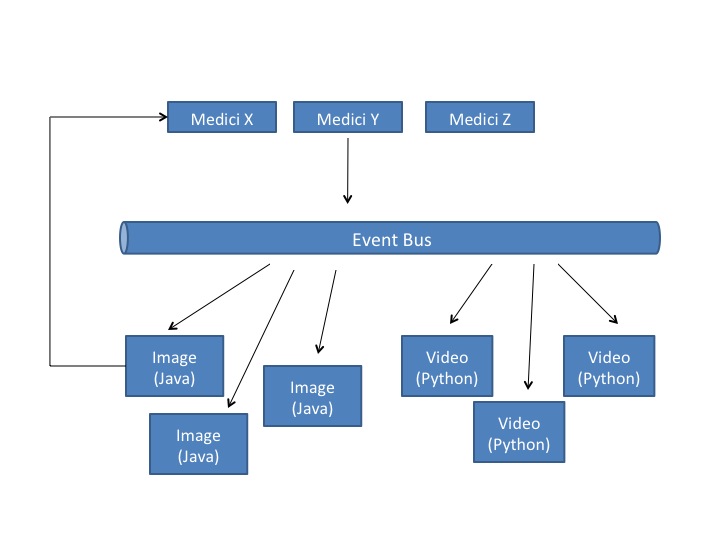
For example, in the case of images, a preprocessing step takes care of creating the previews of the image, but also of extracting EXIF and GPS metadata from the image. If GPS information is available, the web client shows the location of the dataset on a map embedded in the page. By making the clients and preprocessing steps independent the system can grow and adapt to different user communities and research domains.
Medici uses a variety of technologies to accomplish its goals. The overall architecture of a typical deployment looks as follows:
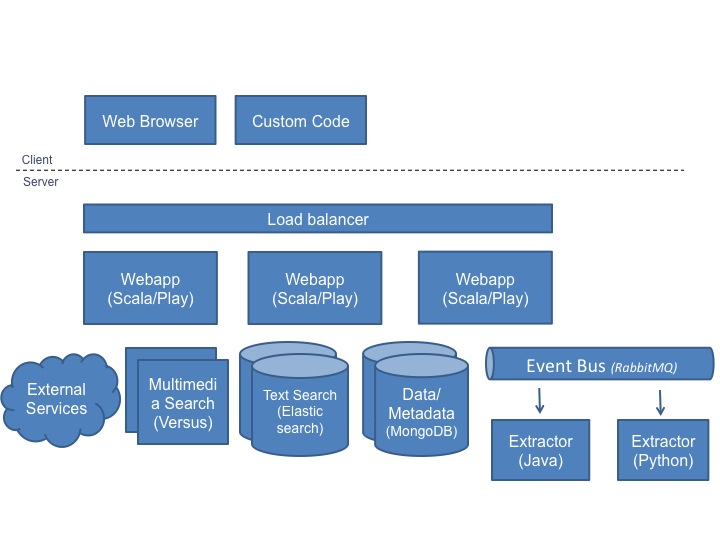
The web application and individual extractors comprise most of the custom Medici code and the core of the system. Most of the other blocks in the diagram are external services Medici depends on. The next section covers how to setup a typical stack.